





6.18 System Interface Coherency

Coherency Conflicts
Coherency conflicts arise when a processor request and an external request target the same secondary cache block. Coherency conflicts may be categorized as either internal or external, and are described in this section.
A processor request is considered to be pending issue when it is buffered in the processor and has not yet been issued to the System interface bus. Internal coherency conflicts occur when the processor has a processor request pending issue and a conflicting external coherency request is received. Internal coherency conflicts are unavoidable and cannot be anticipated by the external agent since it cannot anticipate when the processor will have processor requests pending issue.
Table 6-28 describes the manner in which the processor resolves internal coherency conflicts.
Table 6-28 Internal Coherency Conflict Resolution

 A processor request is considered to be pending response when it has been issued to the System interface bus but has not yet received an external data or completion response. External coherency conflicts occur when the processor has a processor request that is pending response and a conflicting external coherency request is received. The processor relies on the external agent to detect and resolve external coherency conflicts. If the external agent chooses to issue an external coherency request to the processor which causes an external coherency conflict, the external coherency request must be completed before an external response is given to the conflicting processor request. (See page 132 in Errata.)
A processor request is considered to be pending response when it has been issued to the System interface bus but has not yet received an external data or completion response. External coherency conflicts occur when the processor has a processor request that is pending response and a conflicting external coherency request is received. The processor relies on the external agent to detect and resolve external coherency conflicts. If the external agent chooses to issue an external coherency request to the processor which causes an external coherency conflict, the external coherency request must be completed before an external response is given to the conflicting processor request. (See page 132 in Errata.)
External coherency conflicts may be avoided if the point of coherence is the processor System interface bus and only one request is allowed to be outstanding for any given secondary cache block. However, in some system designs external coherency conflicts are unavoidable.
Processor block write and eliminate requests are never pending response, and therefore cannot cause external coherency conflicts.
Table 6-29 describes the manner in which the external agent resolves external coherency conflicts.
Table 6-29 External Coherency Conflict Resolution

 (Revised footnotes in Table 6-29 above; see page 132 in Errata.)
(Revised footnotes in Table 6-29 above; see page 132 in Errata.)
External Coherency Request Latency
This section describes the R10000 external coherency request latency. Figure 6-26 depicts the following:
- an external coherency request which targets the processor
- the resulting processor coherency state response
- the potential processor coherency data response
Two external coherency request latency parameters are also defined:
- the processor coherency state response latency, tpcsr, specifies the time from external coherency request to processor coherency state response
- the processor coherency data response latency, tpcdr, specifies the time from the external coherency request to the processor coherency data response if a master, or to the assertion of the processor coherency data response indication on SysState[0] if a slave.

Figure 6-26 External Coherency Request Latency Parameters
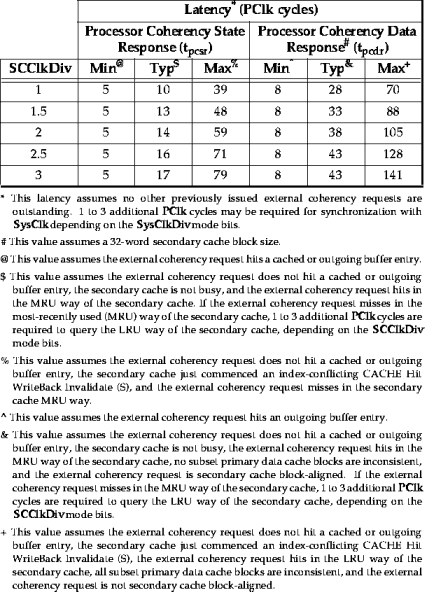
The external coherency request latency is presented in Table 6-30.
Table 6-30 External Coherency Request Latency






Copyright 1995, MIPS Technologies, Inc. -- 29 JAN 96



Generated with CERN WebMaker








![]()
 A processor request is considered to be pending response when it has been issued to the System interface bus but has not yet received an external data or completion response. External coherency conflicts occur when the processor has a processor request that is pending response and a conflicting external coherency request is received. The processor relies on the external agent to detect and resolve external coherency conflicts. If the external agent chooses to issue an external coherency request to the processor which causes an external coherency conflict, the external coherency request must be completed before an external response is given to the conflicting processor request. (See page 132 in Errata.)
A processor request is considered to be pending response when it has been issued to the System interface bus but has not yet received an external data or completion response. External coherency conflicts occur when the processor has a processor request that is pending response and a conflicting external coherency request is received. The processor relies on the external agent to detect and resolve external coherency conflicts. If the external agent chooses to issue an external coherency request to the processor which causes an external coherency conflict, the external coherency request must be completed before an external response is given to the conflicting processor request. (See page 132 in Errata.)![]()
 (Revised footnotes in Table 6-29 above; see page 132 in Errata.)
(Revised footnotes in Table 6-29 above; see page 132 in Errata.)![]()








